
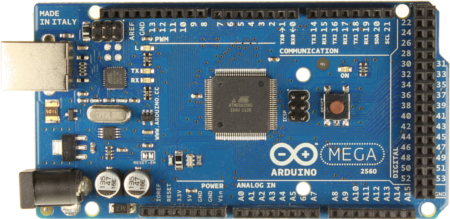
Thanks to its large number of GPIO pins, the ATMega2560 overcomes the limitations of smaller microcontrollers like the ATMega328P and allows it to communicate with more sensors and peripherals, while also leaving a large number of GPIO pins available for other tasks.

This is not a major limitation, it can be overcome using level shifting circuits. The ATMega2560 uses 5V logic levels, so it might not be compatible with 3.3V sensors and other peripherals. Port registers allow for lower-level and faster manipulation of the i/o pins of the microcontroller on an Arduino board. The GPIO pins are also mapped internally to the peripherals like SPI, USART, and SPI. Finally after setting the board as 'Arduino/Genuino Mega 2560, ATmega2560(Mega 2560)', in Arduino IDE, I pushed the below sketch on the board. 4ON and rest OFF), and finally the other switch set to TXD3/RXD3. The easiest to use is the Arduino Mega board, which contains the ATMega3560, and can be programmed over USB from the Arduino software. Though the same chip works with a Nano in same pin configuration. It can be programmed using Atmel Studio and a dedicated programmer, or using another ATMega microcontroller and using the Arduino development environment. The ATMega2560 is an 8-bit AVR microcontroller that comes with 86 programmable GPIO pins, PWM, ADC, and timer peripherals. Note: Complete technical details can be found in the ATMega2560 datasheet given at the end of this page. Two 8-bit timer/counters, four 16-bit timer/counters.It can be clocked up to 16MHz with a 5V supply. It also has a wide variety of peripherals, including timers, counters, PWM generators, a comparator, and ADCs. It is based on the 8-bit AVR RISC architecture and has 256KB flash memory, 8KB SRAM, and 4KB EEPROM. These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value. The ATMega2560 from Atmel is an 8-bit low-power microcontroller that is found in the popular Arduino Mega development board.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
